Nearshoring vs. Farshoring: Which One is Better for Your Business?
In today's global economy, businesses are increasingly turning to outsourcing to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain access to specialized expertise. Two popular approaches to outsourcing are nearshoring and farshoring, which involve outsourcing to nearby and distant countries.
While both approaches offer advantages, they also come with their own set of challenges. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between nearshoring and farshoring and help you determine which approach is best for your business.
What is farshoring?
Farshoring is the practice of outsourcing business processes or services to a distant country, often intending to reduce costs. For example, a company based in the United Kingdom might farshore its customer service operations to India or the Philippines.
Benefits of farshoring
The main advantage of farshoring is that it offers lower labor costs than nearshoring, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to reduce costs. Farshoring also allows companies to access a wider pool of skilled workers and take advantage of different time zones to provide round-the-clock service.
Other benefits of farshoring include:
- access to specialized expertise;
- increased flexibility and scalability.
Challenges of farshoring
While farshoring can offer lower costs and access to a broader pool of skilled workers, it also comes with challenges. One of the biggest is the cultural and linguistic barriers that can make communication and collaboration difficult.
Other challenges of farshoring include:
- time zone differences that can make collaboration and communication difficult;
- longer shipping and delivery times;
- political instability or economic uncertainty in the region;
- data security and privacy concerns.
Let's take a look at real-life examples to see some shortcomings of farshoring.
The clothing brand Levi Strauss has been farshoring its manufacturing to various countries in Asia, including China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh. While this has allowed the company to take advantage of lower labor costs, it has faced challenges such as working conditions and labor rights violations in some countries.
Also, back in 2013, the clothing company, Primark, faced controversy over labor rights violations in its suppliers' factories in Bangladesh. The factories produced clothes for Primark at a much lower cost than in Europe, but the workers were paid extremely low wages and worked in hazardous conditions. This farshoring strategy resulted in a public relations crisis for the company and raised concerns about the ethical implications of offshoring manufacturing to countries with weaker labor standards.
More and more companies turn to nearshoring as an alternative for their business to avoid similar problems.
According to the latest JLL report on Supply Chain Disruptions, Europe is set to experience a surge in nearshoring due to disruptions in the supply chain in Ukraine and Asia.
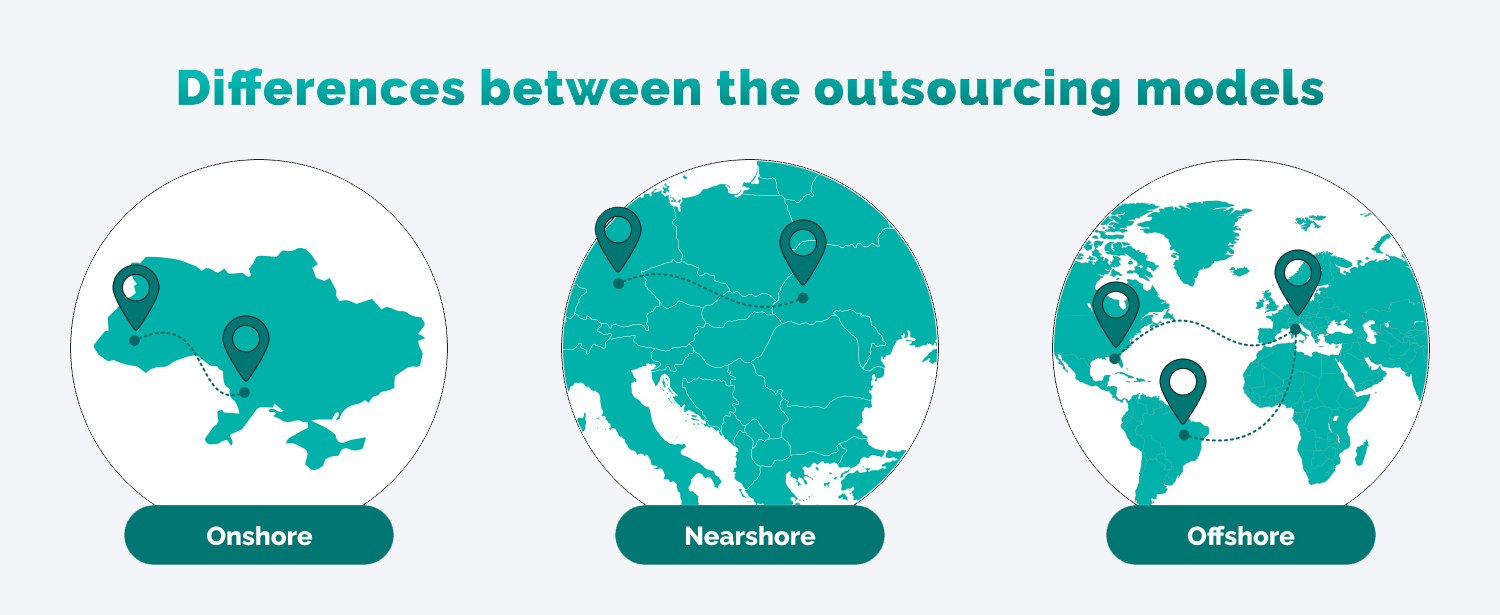
What is nearshoring?
Nearshoring is outsourcing business processes or services to a nearby country, often to reduce costs and improve efficiency. For example, a company based in Germany might choose to nearshore its customer service operations to neighboring countries in Europe.
Benefits of nearshoring
When it comes to the benefits of nearshoring, it is worth considering the following pros:
- Nearshoring allows businesses to access a pool of skilled workers at a lower cost than hiring locally.
- Nearshoring enables businesses to take advantage of a shared time zone, cultural similarities, and language proficiency, which can improve communication and collaboration between teams.
- Reduced risk of supply chain disruption. As the companies outsource services from nearby locations, they minimize the impact of external factors such as natural disasters or geopolitical instability.
- Reduced risk of data breaches. Data security is a major concern for companies, and nearshoring to countries that are members of the European Union can mitigate this risk due to the implementation of uniform data protection regulations.
To see how nearshoring works in practice, let's look at the Swiss pharmaceutical and biotech company Novartis, which specializes in drug research, development, and manufacturing.
Novartis has nearshored its drug development operations to Hungary, which shares a culture and time zone with Switzerland, where the company is headquartered.
The nearshoring strategy has allowed Novartis to tap into Hungary's large pool of highly educated scientists and researchers while taking advantage of the country's lower labor costs compared to Switzerland. Additionally, the proximity between Hungary and Switzerland allows Novartis to maintain a closer relationship with its research team and to reduce travel time and costs.
Why choose nearshoring for your business?
When deciding between nearshoring and farshoring, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Ultimately, the decision will depend on various factors, including the nature of the business process or service being outsourced, the size and complexity of the operation, and the business's specific needs.
However, when discussing which model is here to stay, we must evaluate the current economic and political situation in Europe and worldwide. According to the latest JLL report on Supply Chain Disruptions, Europe is set to experience a surge in nearshoring due to disruptions in the supply chain in Ukraine and Asia.
Therefore, when looking at the nearest future, nearshoring is a model to stay as it offers the best balance of cost savings and operational efficiency, which add up to the company's overall success, especially during challenging times.
Have a question?
Get in touch!
Baltic Assist provides a comprehensive outsourcing solutions that saves costs, enhances efficiency, and strategic decision-making for your business.



